Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. It involves the development of algorithms and models that enable machines to learn from data, make decisions, and solve problems. AI encompasses various subfields such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. The goal of AI is to create intelligent machines capable of adapting and improving their performance over time.
Curious about the wonders of technology? Ever wondered, How does Artificial Intelligence work? Dive into the fascinating realm of AI, where machines learn, adapt, and make decisions like never before. Uncover the secrets behind this cutting-edge technology that’s shaping the future. Ready to unravel the mysteries of Artificial Intelligence? Join us on a journey of discovery and explore the limitless possibilities. Embrace the future learn how Artificial Intelligence works today!
What Is Artificial Intelligence (Ai)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that aims to create systems capable of performing tasks that normally require human intelligence. These tasks include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and understanding natural language. In essence, AI seeks to build machines that can mimic cognitive functions and enhance efficiency across various applications.
How does AI work?
AI works by utilizing algorithms and data to enable machines to learn from experience, make decisions, and perform tasks without explicit programming. Through processes like machine learning, where systems analyze patterns in data, AI systems improve their performance over time. Essentially, AI operates by replicating human-like cognitive functions to solve problems and handle diverse tasks in an increasingly autonomous manner.
Differences between AI, machine learning and deep learning
AI is the broad field encompassing the development of intelligent systems that can simulate human intelligence. Machine learning is a subset of AI, focusing on algorithms that enable machines to learn from data and make predictions or decisions. Deep learning, another subset of AI, employs neural networks with many layers to learn intricate patterns in data, enabling more complex tasks like image and speech recognition.
Why is artificial intelligence important?

Artificial intelligence is important because it has the potential to revolutionize various industries by improving efficiency, productivity, and decision-making processes. Through automation and optimization, AI can streamline tasks, freeing up human resources for more creative and strategic endeavors. Additionally, AI has the capability to tackle complex problems in areas like healthcare, finance, and transportation, offering innovative solutions that can enhance quality of life and drive economic growth.
Furthermore, Pixelcut AI enables advancements in fields such as personalized medicine, autonomous vehicles, and smart infrastructure, contributing to safer and more sustainable societies. Its ability to analyze vast amounts of data and derive insights empowers businesses and organizations, making informed decisions and staying competitive in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape. In essence, artificial intelligence, including cutting-edge solutions like Pixelcut AI, holds the promise of transforming industries, enhancing human capabilities, and shaping the future of technology and society.
A guide to artificial intelligence in the enterprise
Navigating the realm of artificial intelligence in the enterprise involves harnessing advanced technologies to drive business innovation. From automating routine tasks to optimizing decision-making processes, AI offers solutions that can enhance productivity and competitiveness. This guide provides insights into integrating artificial intelligence effectively, helping businesses leverage its potential for improved efficiency and strategic growth in the dynamic landscape of the modern enterprise.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence comes with various advantages, such as increased efficiency, automation of repetitive tasks, and improved decision-making based on data analysis. It can enhance productivity, reduce operational costs, and contribute to innovative solutions in fields like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. AI’s ability to process vast amounts of information quickly allows for more accurate predictions and personalized experiences, bringing about significant benefits to industries and individuals alike.
However, the deployment of artificial intelligence also raises concerns. Disadvantages include the potential for job displacement due to automation, ethical considerations related to decision-making algorithms, and the risk of biases embedded in AI systems. Additionally, issues regarding data privacy and security pose challenges, as AI systems rely heavily on large datasets. Striking a balance between harnessing the advantages of AI and addressing its drawbacks is crucial for responsible and effective integration into various aspects of society.
Advantages of AI
The advantages of artificial intelligence (AI) are manifold. AI systems can automate mundane and repetitive tasks, saving time and resources for businesses. They excel at processing vast amounts of data, leading to improved decision-making, enhanced efficiency, and innovative solutions across various industries.
Disadvantages of AI
However, the deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) comes with certain disadvantages. Job displacement due to automation raises concerns about unemployment, and ethical issues arise regarding biased decision-making algorithms. Privacy and security challenges emerge as AI relies heavily on large datasets, raising questions about the responsible use of sensitive information. Balancing the benefits of AI with these drawbacks is essential for ensuring ethical and sustainable integration into society.
Strong AI vs. weak AI
| Strong AI | Weak AI | |
| Definition | Possesses human-like cognitive abilities | Designed for specific tasks |
| Capabilities | Can perform any intellectual task that a human can | Limited to a narrow range of tasks |
| Consciousness | May exhibit consciousness and self-awareness | Lacks consciousness and self-awareness |
| Examples | Human-level intelligence | Virtual assistants, chatbots |
| Complexity | Highly complex and adaptable | Relatively simpler and specialized |
This table highlights the distinctions between Strong AI, which aims to replicate human intelligence, and Weak AI, which focuses on narrow, task-specific functionalities.
What are the 4 types of artificial intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence can be categorized into four main types based on its capabilities and functionalities. The first type is Reactive Machines, which operate based on predefined rules and lack the ability to learn or adapt. The second type is Limited Memory AI, where systems can learn from historical data to make better decisions but have a finite memory of the past. The third type is Theory of Mind AI, a more advanced form that can understand human emotions, intentions, and beliefs. Lastly, Self-aware AI represents the highest level, where machines possess consciousness and a sense of self, although achieving this level remains a theoretical concept in current AI development. These categories showcase the progression from rule-based systems to AI with more human-like understanding and awareness.
- Reactive Machines: Operate on predefined rules without the ability to learn or adapt.
- Limited Memory AI: Learns from historical data to make improved decisions but has finite memory.
- Theory of Mind AI: Understands human emotions, intentions, and beliefs, exhibiting a more advanced level of cognitive understanding.
What are examples of AI technology and how is it used today?
AI technology is prevalent in various aspects of our daily lives. Virtual assistants like Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri utilize natural language processing to understand and respond to user commands, making tasks like setting reminders and searching the web more convenient. Recommendation systems employed by streaming services such as Netflix and Spotify analyze user preferences and behavior to suggest personalized content, enhancing the user experience. In healthcare, AI-powered diagnostic tools assist physicians in interpreting medical images and identifying potential abnormalities, leading to earlier detection and improved patient outcomes. Additionally, autonomous vehicles incorporate AI algorithms to navigate roads safely, making transportation more efficient and reducing the risk of accidents.
Moreover, AI is transforming industries such as finance through algorithmic trading, where automated systems analyze market trends and execute trades at high speeds. In manufacturing, robots equipped with machine learning algorithms enhance production efficiency by performing tasks with precision and adaptability. Smart home devices utilize AI to optimize energy usage and enhance security, providing homeowners with greater control and peace of mind. These examples illustrate how AI technology is revolutionizing various sectors and reshaping the way we live, work, and interact with technology.
What are the applications of AI?
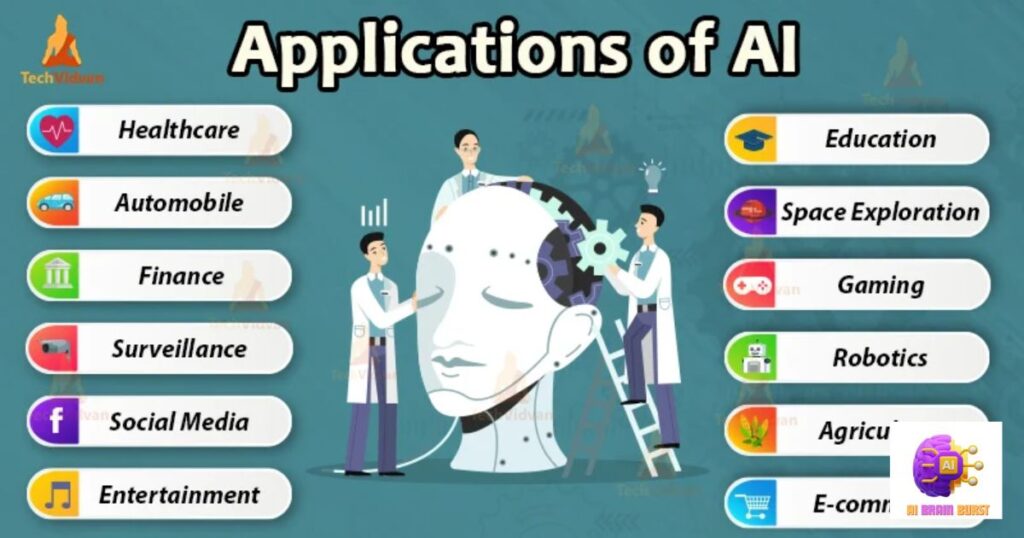
AI finds applications across diverse fields, contributing to advancements and efficiency. In healthcare, AI is utilized for diagnostic purposes, analyzing medical images to detect anomalies and aid in early disease identification. In finance, AI plays a crucial role in fraud detection, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading, enhancing accuracy and security. Virtual assistants like Siri and Google Assistant showcase AI applications in the realm of natural language processing, enabling users to interact with devices through voice commands.
Moreover, AI is prevalent in customer service through chatbots that provide instant responses and personalized assistance. In manufacturing, robots equipped with AI enhance automation by performing complex tasks with precision and adaptability. Smart home devices use AI to learn user preferences, optimizing energy consumption and enhancing overall efficiency. These applications highlight the versatility of AI, showcasing its potential to revolutionize industries, streamline processes, and improve the overall quality of products and services.
Augmented intelligence vs. artificial intelligence
| Augmented Intelligence | Artificial Intelligence | |
| Definition | Enhances human capabilities and decision-making | Seeks to replicate human-like intelligence |
| Collaboration | Collaborative approach, combining human and machine intelligence | Operates autonomously, without direct human involvement |
| Decision-making | Aims to assist and support human decision-making | Designed to make decisions independently based on data and algorithms |
| Human-Centric | Focuses on enhancing human skills and performance | Often aims to replace or replicate human tasks and cognition |
| Example | Predictive analytics tools that assist professionals in decision-making | Fully autonomous vehicles that operate without human intervention |
| Adaptive Capability | Adapts to human input and learns from user interactions | Learns from data and experiences to improve performance over time |
| Context | Centers on the idea of working together with humans for mutual benefit | Concentrates on creating machines with human-like cognitive abilities |
This table highlights the distinctions between Augmented Intelligence, which enhances human capabilities, and Artificial Intelligence, which aims to replicate or replace human-like intelligence.
Ethical use of artificial intelligence
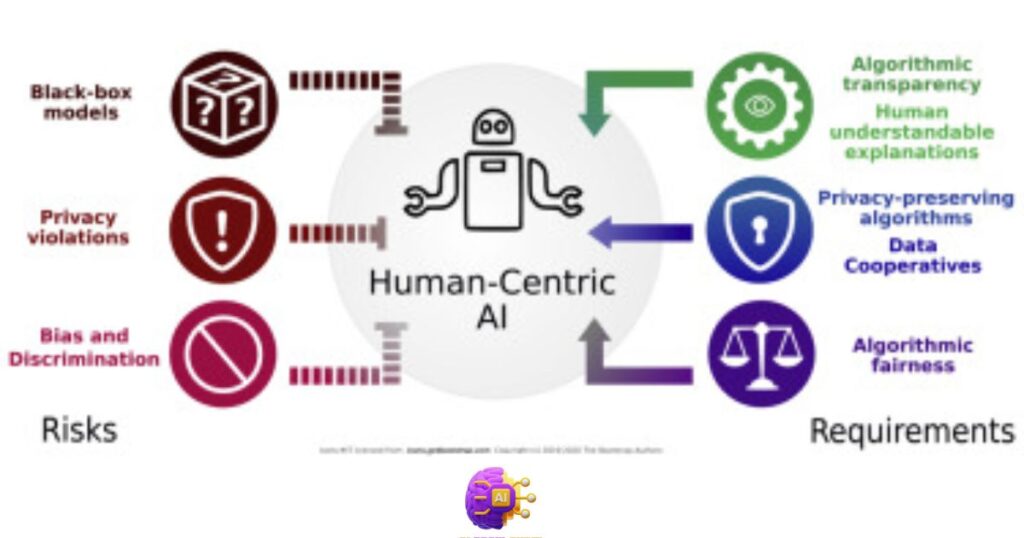
Ensuring the ethical use of artificial intelligence (AI) is paramount as the technology continues to evolve. It involves addressing concerns such as bias in algorithms, data privacy, and the potential impact of AI on employment. Developers and organizations must strive for transparency in AI systems, providing clear insights into how decisions are made and taking measures to avoid reinforcing existing biases.
Additionally, establishing guidelines and regulations for the ethical use of AI is crucial to prevent misuse and promote accountability. Ethical considerations in AI development also involve safeguarding user privacy, securing sensitive data, and fostering inclusivity to avoid discrimination. Striking a balance between innovation and ethical responsibility is essential for the responsible deployment of AI, ensuring its positive impact on society while mitigating potential risks and concerns.
AI governance and regulations
AI governance and regulations are vital components in managing the responsible development and deployment of artificial intelligence (AI). Governments and organizations are increasingly recognizing the need to establish guidelines to address ethical concerns, data privacy, and potential societal impacts. Effective AI governance involves creating frameworks that ensure transparency, accountability, and fairness in the use of AI technologies.
Regulations play a crucial role in setting standards for AI development and deployment, helping to prevent misuse and protect individuals’ rights. These rules may include guidelines for data protection, algorithmic transparency, and ethical considerations. Striking a balance between fostering innovation and safeguarding against potential risks, AI governance and regulations are instrumental in shaping a responsible and beneficial integration of artificial intelligence into various aspects of society.
What is the history of AI?

The history of artificial intelligence (AI) dates back to ancient times, with early philosophical discussions about the nature of human intelligence and the possibility of creating artificial beings. However, the formal beginnings of AI as a field of study emerged in the mid-20th century. In 1956, the term “artificial intelligence” was coined during the Dartmouth Conference, where pioneers like John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and others laid the foundation for AI research.
Over the decades, AI has experienced periods of both enthusiasm and skepticism, known as “AI summers” and “AI winters.” Breakthroughs such as rule-based systems, expert systems, and machine learning algorithms have marked milestones in AI development. Recent years have seen remarkable progress, driven by advances in deep learning, neural networks, and increased computational power. Today, AI is an integral part of various industries, shaping the future of technology with applications ranging from virtual assistants and recommendation systems to autonomous vehicles and advanced healthcare solutions.
AI tools and services

AI tools and services have become essential components in various industries, offering innovative solutions to streamline processes and enhance efficiency. In the business sector, AI-powered analytics tools help organizations gain valuable insights from vast datasets, facilitating informed decision-making. Virtual assistants and chatbots, common AI applications, provide personalized customer interactions and support in sectors like e-commerce and customer service, contributing to improved user experiences.
Moreover, AI services are prevalent in healthcare, aiding in diagnostic processes and treatment planning. Machine learning algorithms analyze medical data to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and assist medical professionals in delivering more accurate and timely care. These AI tools and services showcase the diverse applications of artificial intelligence, transforming the way businesses operate and enhancing the quality of services provided across various sectors.
FAQ’s
How does AI work in daily life?
AI works in daily life through applications like virtual assistants, recommendation systems, and smart devices, simplifying tasks, providing personalized experiences, and contributing to increased efficiency in various aspects of our routine.
What happens if AI takes over?
If AI were to take over, it could potentially lead to significant societal shifts, impacting employment, decision-making processes, and ethical considerations, emphasizing the importance of responsible AI governance and regulation.
Why won’t AI take over the world?
AI won’t take over the world because it lacks autonomy and consciousness; it operates based on programmed algorithms and requires human oversight and control.
What will happen in 2050?
Predicting specific events in 2050 is challenging, but advancements in technology, climate change mitigation efforts, and demographic shifts are likely to shape the world’s landscape.
Is AI harmful in future?
The impact of AI in the future depends on ethical considerations, regulations, and responsible development; if not managed carefully, AI could pose potential risks such as bias, job displacement, and privacy concerns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, artificial intelligence (AI) represents a transformative force with the potential to revolutionize various aspects of society. From streamlining business operations to enhancing healthcare and improving daily convenience, AI offers countless opportunities for innovation and advancement. However, ensuring the responsible development and ethical deployment of AI is essential to mitigate potential risks and maximize its benefits. With careful governance, collaboration, and consideration of societal implications, we can harness the power of AI to create a more efficient, inclusive, and prosperous future for all.
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, embracing the potential of AI requires a balance between innovation and responsibility. As we navigate the complexities of AI integration, it’s crucial to prioritize transparency, accountability, and inclusivity. By fostering a collaborative approach that involves stakeholders from diverse backgrounds and perspectives, we can shape AI to serve humanity’s best interests. Together, we can navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by artificial intelligence, paving the way for a brighter and more equitable future.